Mastering AutoCAD’s Design Center and Tool Palettes: A Comprehensive Guide to Efficient Design Workflows
Introduction: In the realm of computer-aided design (CAD), AutoCAD stands as a powerful tool for architects, engineers, designers, and drafters seeking to create precise and innovative designs. To enhance productivity and streamline workflows, AutoCAD offers a range of features and tools, including the Design Center and Tool Palettes. In this extensive guide, we will delve into the intricacies of using AutoCAD’s Design Center and Tool Palettes, exploring the techniques, functionalities, and best practices to empower users to unlock the full potential of these tools and achieve their design goals with efficiency, accuracy, and creativity.
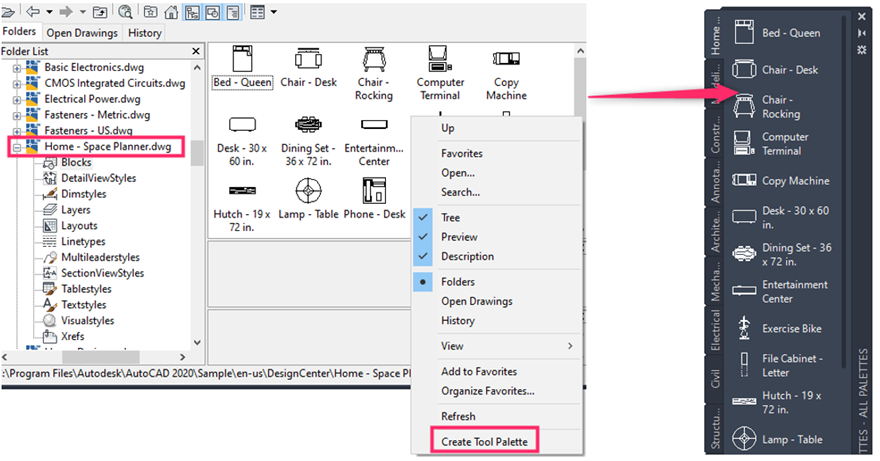
Understanding AutoCAD’s Design Center: AutoCAD’s Design Center is a powerful tool for accessing and managing design content, including blocks, drawings, layers, linetypes, styles, and more. It provides a centralized location for browsing, previewing, and inserting design elements from external sources into the current drawing. The Design Center streamlines the design process by allowing users to reuse existing design components, maintain consistency across drawings, and leverage a vast library of resources to enhance their designs.
Key Features of AutoCAD’s Design Center: Before delving into the process of using AutoCAD’s Design Center, it’s essential to understand some key features that make it a valuable tool for CAD users:
- Content Browser: The Content Browser in the Design Center provides a hierarchical view of design content organized into categories such as Blocks, Drawings, Layers, Linetypes, Materials, Styles, and more. Users can navigate through categories and subcategories, preview content thumbnails, and access detailed information about design elements.
- Preview Pane: The Preview Pane in the Design Center allows users to preview design elements such as blocks, drawings, and styles before inserting them into the current drawing. It provides visual feedback on the appearance, scale, and orientation of design content, enabling users to make informed decisions when selecting and inserting design elements.
- Insertion Options: The Design Center offers various insertion options for inserting design elements into the current drawing, including drag-and-drop, copy-paste, and insert as block. Users can choose the insertion method that best suits their workflow and preferences, ensuring flexibility and efficiency in design tasks.
- Search and Filter: The Design Center includes search and filter options for quickly locating specific design elements within the content browser. Users can search for design elements by name, type, keyword, or attribute, and apply filters to narrow down search results based on criteria such as file type, date modified, or layer name.
Understanding AutoCAD’s Tool Palettes: AutoCAD’s Tool Palettes are customizable panels that provide quick access to frequently used tools, commands, blocks, and macros. They offer a convenient way to organize and access design content, streamline repetitive tasks, and improve productivity in AutoCAD. Tool Palettes can be customized to suit individual preferences and workflows, making them versatile tools for CAD users across various industries and disciplines.
Key Features of AutoCAD’s Tool Palettes: Before exploring the process of using AutoCAD’s Tool Palettes, it’s essential to understand some key features that make them valuable tools for CAD users:
- Customization Options: AutoCAD’s Tool Palettes are highly customizable, allowing users to create, organize, and customize palette tabs, groups, and tools to suit their specific needs and workflows. Users can add, remove, rearrange, and rename palette tabs and groups, as well as customize tool icons, labels, and tooltips for easy identification and access.
- Tool Organization: Tool Palettes provide a flexible way to organize tools, commands, blocks, and macros into logical groups and categories. Users can create palette tabs for different project phases, disciplines, or tasks, and organize tools within each tab into groups based on functionality or usage frequency. This organization helps users quickly locate and access the tools they need, improving efficiency and productivity in AutoCAD.
- Tool Management: AutoCAD’s Tool Palettes offer robust management capabilities for adding, editing, and managing tools, commands, blocks, and macros. Users can add tools to palettes by dragging and dropping from the ribbon, toolbar, command line, or other palette tabs, as well as create custom tools using macros or scripts. Palette tools can be edited, duplicated, or deleted as needed, and tool properties such as icon size, display order, and visibility can be adjusted to optimize usability.
- Tool Properties: Each tool in AutoCAD’s Tool Palettes has associated properties that define its behavior, appearance, and functionality. Users can customize tool properties such as command string, tooltip text, icon image, and command options to tailor tools to specific tasks or preferences. Tool properties can be edited directly within the palette interface, providing a convenient way to fine-tune tool behavior and appearance without the need for complex configuration.
Basic Usage of AutoCAD’s Design Center and Tool Palettes: Using AutoCAD’s Design Center and Tool Palettes involves a series of steps that begin with accessing and organizing design content and culminate in inserting and using design elements in the current drawing. Here’s a basic overview of the usage process for each tool:
Using AutoCAD’s Design Center:
- Accessing the Design Center: Open the Design Center by typing “ADCENTER” in the command line or by selecting “Design Center” from the “View” tab on the ribbon.
- Browsing Design Content: Navigate through the Content Browser in the Design Center to locate and preview design elements such as blocks, drawings, layers, linetypes, and styles.
- Inserting Design Elements: Select the desired design element from the Content Browser, preview it in the Preview Pane, and then insert it into the current drawing using the desired insertion method (e.g., drag-and-drop, copy-paste).
- Customizing Display Options: Customize the display options in the Design Center to adjust thumbnail size, detail level, and content visibility, ensuring an optimal browsing experience.
Using AutoCAD’s Tool Palettes:
- Accessing Tool Palettes: Open the Tool Palettes by typing “TPLT” in the command line or by selecting “Tool Palettes” from the “View” tab on the ribbon.
- Organizing Tool Palettes: Create and organize palette tabs and groups to categorize tools based on functionality, project phase, or discipline. Add, remove, and rearrange tools within each group to optimize usability.
- Adding Tools to Palettes: Add tools to palettes by dragging and dropping from the ribbon, toolbar, command line, or other palette tabs. Customize tool properties such as icon image, tooltip text, and command string to tailor tools to specific tasks or preferences.
- Using Tools in Drawings: Select the desired tool from the palette, then click or drag in the drawing area to execute the tool command. Adjust tool options and parameters as needed using the command line or tool properties palette.
Advanced Usage of AutoCAD’s Design Center and Tool Palettes: While the basic usage of AutoCAD’s Design Center and Tool Palettes suffices for most applications, mastering advanced techniques can enhance productivity, efficiency, and customization in design workflows. Here are some advanced techniques and applications to consider:
Advanced Usage of AutoCAD’s Design Center:
- Custom Content Sources: Configure custom content sources in the Design Center to access design content from external locations such as network drives, cloud storage, or project folders. Define source paths and file types to include in the Content Browser, providing easy access to project-specific resources.
- Batch Insertion: Use batch insertion techniques in the Design Center to insert multiple design elements into the current drawing simultaneously. Select multiple items in the Content Browser, then drag and drop them into the drawing area to insert them as separate entities or blocks.
- Content Management: Manage design content in the Design Center by organizing, renaming, and categorizing design elements into custom folders and subfolders. Create shortcuts to frequently used content, and update content thumbnails and descriptions to improve usability and accessibility.
Advanced Usage of AutoCAD’s Tool Palettes:
- Custom Tool Creation: Create custom tools in Tool Palettes using macros, scripts, or custom commands to automate repetitive tasks or execute complex workflows. Define tool properties such as command string, icon image, and tooltip text to customize tool behavior and appearance.
- Dynamic Blocks and Parametric Tools: Incorporate dynamic blocks and parametric tools into Tool Palettes to create intelligent design elements that adapt dynamically to changes in geometry or parameters. Define block attributes, parameters, and actions to create flexible and reusable design components that enhance productivity and design efficiency.
- Palette Customization: Customize Tool Palettes using advanced palette customization techniques such as XML editing, palette configurations, and template files. Modify palette properties, layout settings, and palette tabs to create custom palette layouts tailored to specific project requirements or user preferences.
Best Practices for Using AutoCAD’s Design Center and Tool Palettes: To achieve optimal results when using AutoCAD’s Design Center and Tool Palettes, consider the following best practices:
- Organize Design Content: Organize design content in the Design Center and Tool Palettes into logical categories and groups to facilitate easy navigation and access. Use descriptive names, thumbnails, and tooltips to provide context and information about design elements, enhancing usability and efficiency in design workflows.
- Customize Interface Layout: Customize the interface layout of the Design Center and Tool Palettes to suit individual preferences and workflows. Arrange palette tabs, groups, and tools in a logical order, and customize display options such as icon size, text labels, and tooltips to optimize usability and accessibility.
- Maintain Consistency: Maintain consistency across design content in the Design Center and Tool Palettes to ensure uniformity and accuracy in design workflows. Use standardized naming conventions, file structures, and content organization principles to promote consistency and coherence in design elements.
- Update and Refresh Content: Regularly update and refresh design content in the Design Center and Tool Palettes to incorporate new additions, revisions, or improvements. Remove outdated or obsolete content, and update thumbnails, descriptions, and metadata to reflect changes and ensure accuracy and relevance in design workflows.
Conclusion: AutoCAD’s Design Center and Tool Palettes offer powerful tools and features for accessing, managing, and inserting design content into drawings with efficiency and flexibility. By mastering the techniques, functionalities, and best practices for using these tools, users can enhance productivity, streamline workflows, and achieve their design goals with precision and creativity. Whether you’re a novice or an experienced CAD user, the ability to leverage AutoCAD’s Design Center and Tool Palettes empowers you to optimize your design workflows and realize your design visions with confidence and success. With practice, experimentation, and a commitment to continuous improvement, you can harness the full potential of these tools to achieve outstanding results in today’s dynamic design environments.