Exploring the Depths of Color Models in CorelDRAW: A Comprehensive Guide
Introduction: CorelDRAW, a powerful vector graphics editor developed by Corel Corporation, stands as a go-to tool for designers and artists alike. Among its myriad features, the handling of colors plays a pivotal role in shaping the visual appeal of designs. Understanding color models is crucial for achieving precision and creativity in digital artwork. In this comprehensive guide, we delve deep into the world of color models in CorelDRAW, exploring their nuances, applications, and how they contribute to the creation of vibrant and captivating designs.
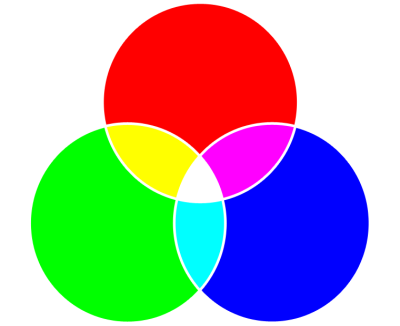
I. Basics of Color Models: Color models serve as mathematical representations of colors, providing a standardized way to describe and reproduce them across various devices. CorelDRAW supports several color models, each with its unique characteristics. The three primary color models in CorelDRAW are RGB (Red, Green, Blue), CMYK (Cyan, Magenta, Yellow, Key/Black), and HSL (Hue, Saturation, Lightness).
A. RGB Color Model:
- Fundamentals: RGB is an additive color model, where colors are created by combining varying intensities of red, green, and blue light. In CorelDRAW, RGB is commonly used for on-screen designs, such as web graphics and digital illustrations.
- Applications: RGB is ideal for projects intended for display on electronic screens, as it accurately represents the colors emitted by electronic devices.
B. CMYK Color Model:
- Basics: CMYK is a subtractive color model used in print design. It involves combining varying percentages of cyan, magenta, yellow, and black inks to achieve a broad spectrum of colors. CorelDRAW users often employ CMYK for projects destined for physical printing.
- Importance in Printing: As CMYK corresponds to the ink colors used in printing, it is essential for ensuring accurate color reproduction in the final printed output.
C. HSL Color Model:
- Overview: HSL represents colors based on their Hue, Saturation, and Lightness. It provides a more intuitive way of manipulating colors, allowing designers to adjust the tone and intensity with ease.
- Creative Control: HSL is frequently used when precise control over color variations is required, providing a versatile approach to color adjustments.
II. Color Modes in CorelDRAW: Understanding color models goes hand in hand with grasping the concept of color modes in CorelDRAW. The software offers different color modes to cater to diverse design requirements.
A. Design Color Mode:
- RGB and CMYK in Harmony: CorelDRAW allows users to work in both RGB and CMYK color modes within the same document. This versatility is beneficial when creating designs intended for both digital and print platforms.
B. Palette Color Mode:
- Indexed Color Palette: CorelDRAW facilitates the creation of indexed color palettes, streamlining the design process. This mode is particularly useful when working with limited color options or designing for specific devices.
III. Advanced Color Management: CorelDRAW’s commitment to precision extends to its advanced color management tools. Designers can take advantage of these features to ensure consistency across different devices and outputs.
A. Spot Colors:
- Definition: Spot colors are pre-mixed inks, providing precise and consistent color reproduction. CorelDRAW supports spot colors, allowing designers to specify exact shades for branding or specific printing requirements.
B. Color Styles:
- Streamlining Workflow: Color Styles in CorelDRAW enable designers to create and manage color schemes efficiently. Changes made to a Color Style are automatically reflected throughout the entire design, enhancing consistency and workflow efficiency.
IV. Challenges and Solutions: While mastering color models in CorelDRAW opens up a world of creative possibilities, it’s essential to address common challenges faced by designers.
A. Color Conversion Challenges:
- RGB to CMYK: Converting RGB designs to CMYK for printing can lead to color discrepancies. CorelDRAW’s color management tools provide options for handling such conversions, ensuring accurate representation.
B. Print vs. Digital Discrepancies:
- Bridging the Gap: Designers often face challenges when transitioning from on-screen to print. CorelDRAW’s simulation modes and soft proofing features aid in visualizing how colors will appear in the final printed output.
Conclusion: Color models in CorelDRAW serve as the backbone of digital design, offering a rich tapestry of possibilities for artists and designers. By understanding the nuances of RGB, CMYK, and HSL color models, mastering color modes, and leveraging advanced color management tools, designers can create visually stunning and consistent artwork that resonates across various mediums. CorelDRAW’s commitment to providing a comprehensive suite of color-related features empowers users to explore their creative boundaries and bring their artistic visions to life with unparalleled precision.