Mastering Sheet Sets in AutoCAD: A Comprehensive Guide to Organizing, Managing, and Streamlining Drawing Sets
Introduction: In the realm of computer-aided design (CAD), AutoCAD stands as a cornerstone tool for architects, engineers, designers, and drafters seeking to create precise and comprehensive drawings. As projects grow in complexity and scale, managing multiple drawings, layouts, and sheets can become a daunting task. Enter sheet sets—a powerful feature in AutoCAD designed to streamline the organization, management, and production of drawing sets. In this extensive guide, we will delve into the intricacies of working with sheet sets in AutoCAD, exploring the techniques, tools, and best practices to empower users to unlock the full potential of sheet sets and realize their design workflows with efficiency, consistency, and precision.
Understanding Sheet Sets in AutoCAD: Sheet sets in AutoCAD are collections of drawing sheets organized hierarchically to represent a complete drawing set for a project or design. Sheet sets provide a centralized location for managing drawing layouts, viewports, annotations, and other sheet-related data, allowing users to organize, navigate, and publish drawing sets with ease. By mastering the techniques for working with sheet sets, users can streamline their design workflows, improve collaboration, and enhance productivity while maintaining consistency and accuracy across drawing sets.
Key Concepts in Sheet Sets: Before delving into the process of working with sheet sets, it’s essential to understand some key concepts that underpin sheet set functionality in AutoCAD:
- Sheet Set Structure: Sheet sets are organized hierarchically into a structure consisting of sheet set properties, subsets, and sheets. Sheet set properties define project information, such as project name, number, and description. Subsets group related sheets within the sheet set, such as discipline-specific subsets (e.g., architectural, structural, mechanical). Sheets represent individual drawing layouts or model views within the sheet set, each containing one or more viewports, annotations, and other sheet-related data.
- Sheet Set Data: Sheet sets contain various types of data, including sheet set properties, sheet set views, sheet set fields, and sheet set custom properties. Sheet set properties include project-specific information such as project name, number, and description. Sheet set views represent saved views of the sheet set structure, allowing users to customize sheet set display and organization. Sheet set fields are placeholders for dynamic text that automatically update based on sheet set properties or system variables. Sheet set custom properties are user-defined properties that allow for additional metadata or project-specific information to be associated with sheets within the sheet set.
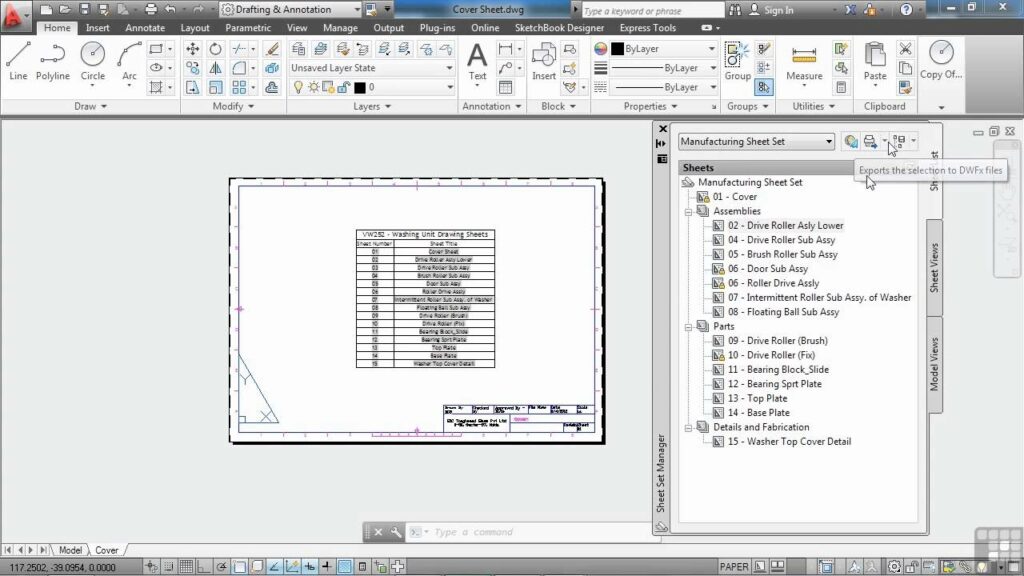
- Sheet Set Manager: The Sheet Set Manager (SSM) is the primary interface for creating, organizing, and managing sheet sets in AutoCAD. The SSM provides access to sheet set properties, subsets, sheets, views, fields, and custom properties, allowing users to perform tasks such as creating new sheet sets, adding sheets to sheet sets, modifying sheet set properties, and publishing drawing sets.
- Sheet Set Publishing: Sheet sets facilitate the production and publishing of drawing sets by providing tools for batch plotting, printing, and publishing. Users can publish drawing sets directly from the Sheet Set Manager interface, specifying output settings such as plot styles, page setups, and file formats. Sheet sets streamline the publishing process by automating tasks such as sheet selection, layout arrangement, and output configuration, saving time and effort while ensuring consistency and accuracy in published drawing sets.
Basic Sheet Set Management Techniques: Working with sheet sets in AutoCAD involves a series of steps that begin with creating and organizing sheet sets and culminate in publishing drawing sets. Here’s a basic overview of the techniques for working with sheet sets:
- Create Sheet Sets: Start by creating sheet sets using the Sheet Set Manager interface. Open the Sheet Set Manager (SSM) palette, create a new sheet set file, and specify sheet set properties such as project name, number, and description. Define subsets to group related sheets within the sheet set, such as discipline-specific subsets (e.g., architectural, structural, mechanical).
- Add Sheets to Sheet Sets: Add sheets to sheet sets by selecting existing drawing layouts or model views and adding them to the sheet set structure. Use the “Add Sheet” command in the Sheet Set Manager interface to specify sheet properties such as sheet number, name, and subset membership. Arrange sheets hierarchically within subsets to organize drawing sets logically and efficiently.
- Manage Sheet Set Properties: Manage sheet set properties such as project information, custom properties, and fields using the Sheet Set Manager interface. Update sheet set properties as needed to reflect project changes, revisions, or updates. Use sheet set fields to automate the insertion of dynamic text based on sheet set properties or system variables, ensuring consistency and accuracy across drawing sets.
- Publish Drawing Sets: Publish drawing sets from the Sheet Set Manager interface by specifying output settings such as plot styles, page setups, and file formats. Select sheets to include in the drawing set, arrange layouts or views on output sheets, and configure output options such as plot scale, orientation, and paper size. Publish drawing sets to plotter devices, printers, or digital files, ensuring that output meets project requirements and standards.
Advanced Sheet Set Management Techniques: While the basic sheet set management techniques suffice for most applications, mastering advanced techniques can enhance the organization, customization, and automation of sheet sets in AutoCAD. Here are some advanced techniques and applications to consider:
- Customizing Sheet Set Properties: Customize sheet set properties and fields to include additional metadata or project-specific information. Define custom properties to capture project-specific data such as client name, project phase, or drawing revision. Use custom fields to insert dynamic text based on sheet set properties or system variables, providing context and information to stakeholders.
- Automating Sheet Set Tasks: Automate sheet set tasks using scripting, macros, or AutoLISP programming. Create scripts or macros to perform repetitive tasks such as creating sheet sets, adding sheets to sheet sets, or publishing drawing sets. Use AutoLISP programming to extend sheet set functionality by adding custom commands, tools, or utilities, enhancing productivity and efficiency in sheet set management.
- Collaborating with Sheet Sets: Collaborate with team members and stakeholders using shared sheet sets and networked Sheet Set Manager projects. Store sheet set files on network drives or cloud storage platforms accessible to project team members, ensuring that everyone has access to the latest sheet set data. Use shared sheet sets to facilitate collaboration, coordination, and communication among project stakeholders, streamlining project workflows and improving project outcomes.
- Integrating Sheet Sets with Other Applications: Integrate sheet sets with other applications or project management tools to streamline project workflows and data exchange. Export sheet set data to spreadsheet formats such as CSV or XLS for analysis, reporting, or integration with project management software. Import sheet set data from external sources to update sheet set properties, fields, or custom properties, ensuring consistency and accuracy in project documentation and reporting.
Best Practices for Sheet Set Management: To achieve optimal results when working with sheet sets in AutoCAD, consider the following best practices:
- Plan and Organize: Start with a clear plan and organizational structure for your sheet sets, including project naming conventions, subset definitions, and sheet numbering schemes. Establish standard practices and procedures for creating, organizing, and managing sheet sets to ensure consistency and accuracy across projects.
- Standardize Sheet Set Properties: Standardize sheet set properties such as project information, custom properties, and fields to ensure consistency and accuracy across drawing sets. Define standard values for common properties such as project name, number, and description, and use custom properties to capture additional project-specific data as needed.
- Document Workflows: Document sheet set workflows, procedures, and best practices to guide users and stakeholders in working with sheet sets. Create user guides, training materials, or process documentation to provide step-by-step instructions, tips, and troubleshooting information for common sheet set tasks and workflows.
- Backup and Archive: Regularly backup and archive sheet set files to prevent data loss and ensure data integrity. Store backup copies of sheet set files on secure storage devices or cloud storage platforms, and establish archiving procedures to retain historical versions of sheet sets for reference, audit, or compliance purposes.
Conclusion: Sheet sets in AutoCAD offer a powerful means of organizing, managing, and publishing drawing sets with efficiency, consistency, and precision. By mastering the techniques, tools, and best practices for working with sheet sets, users can streamline their design workflows, improve collaboration, and enhance productivity while maintaining accuracy and integrity across drawing sets. Whether you’re creating architectural plans, engineering drawings, or construction documents, the ability to work with sheet sets in AutoCAD empowers you to realize your design vision with efficiency and confidence. With practice, experimentation, and attention to detail, you can harness the full potential of sheet sets to organize, manage, and streamline your drawing sets, ensuring success in today’s dynamic design environments.