How to install a motherboard standoff
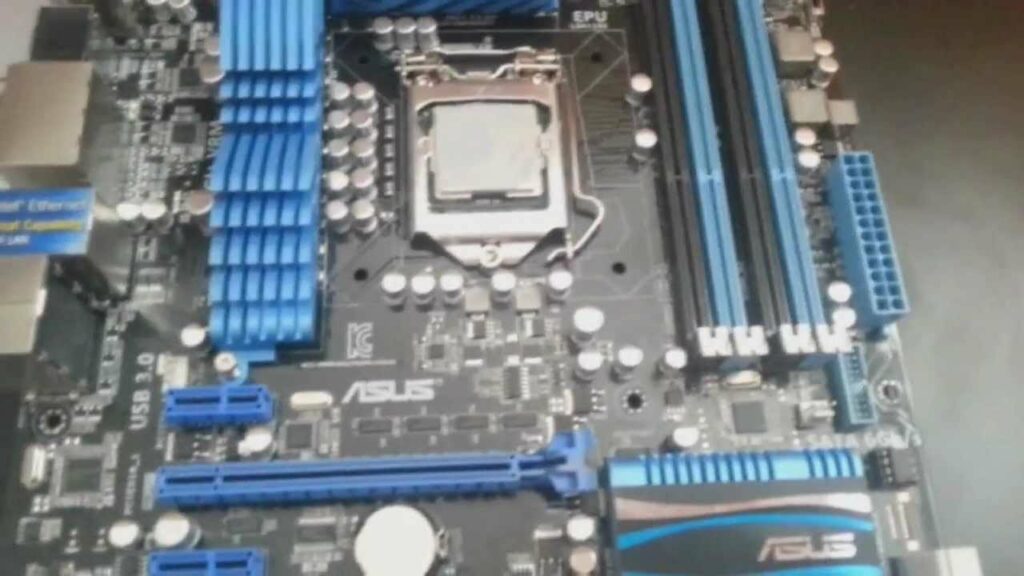

Installing motherboard standoffs is a crucial step in building a PC, ensuring that the motherboard is properly secured and electrically insulated from the case. Standoffs prevent the motherboard from touching the case directly, which can cause electrical shorts and damage. This comprehensive guide will take you through the entire process, from understanding what standoffs are to step-by-step installation and troubleshooting.
Table of Contents
- Understanding Motherboard Standoffs
- Why Standoffs are Important
- Types of Motherboard Standoffs
- Pre-Installation Preparation
- Tools and Materials Needed
- Identifying Standoff Locations
- Safety Precautions
- Step-by-Step Installation Guide
- Preparing the Case
- Installing the Standoffs
- Securing the Motherboard
- Post-Installation Steps
- Verifying Installation
- Connecting Components
- Checking System Functionality
- Troubleshooting Common Issues
- Misaligned Standoffs
- Loose or Missing Standoffs
- Motherboard Not Powering On
- Best Practices for Motherboard Installation and Maintenance
- Conclusion
1. Understanding Motherboard Standoffs
Motherboard standoffs are small metal or plastic spacers that create a gap between the motherboard and the case. They typically come in brass or plastic and are threaded to match the screws that secure the motherboard. Standoffs are essential for proper motherboard installation, ensuring it is securely mounted while avoiding contact with the metal case.
2. Why Standoffs are Important
Standoffs play several critical roles in a PC build:
- Electrical Insulation: They prevent the motherboard from shorting out by keeping it off the metal case.
- Structural Support: Standoffs provide a stable mounting point, preventing the motherboard from flexing or bending.
- Proper Alignment: They ensure that the motherboard’s ports align correctly with the case’s I/O shield and expansion slots.
- Airflow and Cooling: Creating a gap between the motherboard and the case allows for better airflow, which aids in cooling.
3. Types of Motherboard Standoffs
There are several types of standoffs, each suited for different cases and motherboards:
- Brass Standoffs: The most common type, brass standoffs are durable and provide excellent electrical insulation.
- Plastic Standoffs: Used in some cases, these are less conductive and can be easier to install but are not as strong as brass.
- Snap-In Standoffs: These plastic standoffs snap into place without screws, used in some tool-less cases.
4. Pre-Installation Preparation
Tools and Materials Needed
- Motherboard standoffs (usually provided with the case)
- Phillips-head screwdriver
- Tweezers or needle-nose pliers (optional for handling small parts)
- Anti-static wrist strap (optional but recommended)
- Flashlight (for better visibility inside the case)
Identifying Standoff Locations
- Read the Manual: Consult both the motherboard and case manuals to identify the correct standoff locations.
- Match the Form Factor: Ensure that the standoffs correspond to the motherboard’s form factor (ATX, Micro-ATX, Mini-ITX).
- Count the Holes: Count the mounting holes on the motherboard and match them with the standoff locations in the case.
Safety Precautions
- Power Off and Unplug: Ensure the PC is powered off and unplugged from the power source.
- Discharge Static Electricity: Use an anti-static wrist strap or touch a grounded metal object to prevent static discharge.
- Organize Your Workspace: Work in a clean, well-lit area to avoid losing small screws and standoffs.
5. Step-by-Step Installation Guide
Preparing the Case
- Remove the Side Panel: Remove the side panel of your case to access the internal area.
- Clean the Interior: Ensure the inside of the case is clean and free of dust or debris.
- Locate Standoff Points: Identify the standoff points in the case. These are usually marked with small indentations or labels.
Installing the Standoffs
- Position the Standoffs: Align the standoffs with the corresponding holes in the case based on the motherboard’s form factor.
- Screw in the Standoffs: Use a Phillips-head screwdriver to screw in the standoffs. Ensure they are firmly secured but do not overtighten.
- Double-Check Alignment: Verify that all standoffs align with the motherboard’s mounting holes.
Securing the Motherboard
- Insert the I/O Shield: Install the I/O shield (provided with the motherboard) into the rear panel of the case.
- Place the Motherboard: Carefully position the motherboard over the standoffs, ensuring the I/O ports fit through the I/O shield.
- Align the Holes: Align the motherboard’s mounting holes with the standoffs.
- Insert Screws: Insert screws into the mounting holes and secure the motherboard to the standoffs. Tighten the screws in a diagonal pattern to ensure even pressure.
6. Post-Installation Steps
Verifying Installation
- Check Stability: Ensure the motherboard is securely fastened and does not move or flex.
- Inspect Alignment: Verify that all ports and expansion slots are properly aligned.
Connecting Components
- Power Connections: Connect the 24-pin ATX power connector and any additional power connectors (e.g., CPU power).
- Peripheral Connections: Connect any additional components such as GPU, RAM, storage devices, and fans.
Checking System Functionality
- Power On: Power on the system to ensure the motherboard receives power and the system boots.
- BIOS/UEFI Check: Enter the BIOS/UEFI to verify that all components are recognized and functioning correctly.
7. Troubleshooting Common Issues
Misaligned Standoffs
- Solution: Loosen the screws slightly and adjust the motherboard’s position. Ensure all standoffs are properly aligned and secured.
Loose or Missing Standoffs
- Solution: Double-check all standoff locations and ensure none are missing. Tighten any loose standoffs.
Motherboard Not Powering On
- Solution: Verify all power connections are secure. Ensure the power supply is functioning. Check for any shorts or loose components.
8. Best Practices for Motherboard Installation and Maintenance
- Regular Inspections: Periodically check the motherboard and standoffs for any signs of wear or damage.
- Cleaning: Keep the inside of the case clean to prevent dust buildup, which can affect performance and cooling.
- Cable Management: Organize cables to ensure proper airflow and reduce clutter inside the case.
9. Conclusion
Installing motherboard standoffs is a fundamental step in building a PC, providing essential support and insulation for the motherboard. By following this detailed guide, you can ensure a successful installation, protecting your components and ensuring reliable performance. Proper installation and maintenance of standoffs can prevent many common issues and contribute to the longevity and stability of your PC build. Take your time, follow the steps carefully, and double-check your work to achieve the best results. With a well-installed motherboard, you can enjoy a smooth and trouble-free computing experience.