Windows 7: A Comprehensive Guide for Getting Started with the Operating System
Introduction:
Windows 7, released by Microsoft in October 2009, quickly became a hallmark operating system known for its stability, user-friendly interface, and enhanced features. As the successor to Windows Vista, Windows 7 addressed many of the concerns and criticisms of its predecessor, providing users with a more refined and efficient computing experience. In this comprehensive guide, we will delve into the essential aspects of getting started with Windows 7, exploring its installation process, user interface, customization options, security features, and more.
Chapter 1: Installation and System Requirements
Before diving into the functionalities of Windows 7, it’s crucial to understand the installation process and system requirements. Windows 7 is designed to run on a variety of hardware configurations, but it’s essential to ensure your computer meets the minimum specifications. The installation process is straightforward, guided by an intuitive setup wizard that walks you through the necessary steps, including selecting a language, region, and keyboard input.
We will discuss the various editions of Windows 7, such as Home Premium, Professional, and Ultimate, highlighting the unique features each edition offers. Additionally, we’ll explore the upgrade options for users transitioning from earlier Windows versions.
Chapter 2: User Interface and Desktop Experience
Windows 7 introduces a sleek and visually appealing user interface that builds upon the Aero Glass design introduced in Windows Vista. The desktop experience is enhanced with features like the redesigned taskbar, Jump Lists, and Aero Peek. We’ll guide you through the process of navigating the desktop, managing open windows, and utilizing the new taskbar functionalities to streamline your workflow.
Customization is a significant aspect of the Windows 7 user interface. We’ll explore how to personalize your desktop by changing themes, wallpapers, and window colors. Additionally, we’ll discuss the desktop gadgets that provide at-a-glance information, and how to customize them to suit your preferences.
Chapter 3: File Management and Libraries
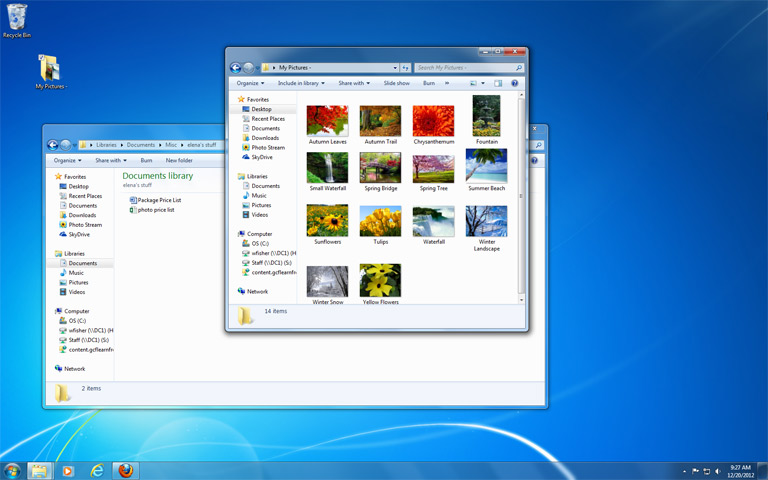
Windows 7 improves file management with the introduction of Libraries, a feature that allows users to organize and access their files more efficiently. We’ll explain how Libraries work, how to create and manage them, and how they can simplify the process of organizing and finding your documents, pictures, music, and videos.
The revamped Windows Explorer, now known as File Explorer, is another crucial aspect of file management in Windows 7. We’ll guide you through the various features of File Explorer, including the Quick Access view, the ribbon interface, and the powerful search capabilities.
Chapter 4: Networking and Internet Connectivity
Windows 7 comes equipped with enhanced networking capabilities, making it easier to connect to both wired and wireless networks. We’ll walk you through the process of setting up and managing network connections, sharing files and printers, and troubleshooting common networking issues.
Internet Explorer 8, the default web browser in Windows 7, introduces improved security features and a more streamlined user interface. We’ll explore the browser’s features, including tabbed browsing, accelerators, and web slices, and discuss how to enhance your online experience.
Chapter 5: Security and Maintenance
One of the key priorities for any operating system is ensuring the security of user data and the overall system. Windows 7 introduces several security features and improvements over its predecessors. We’ll delve into User Account Control (UAC), Windows Firewall, and Windows Defender, discussing how to configure these tools to enhance your system’s security.
Windows Update is a critical component of maintaining a secure and up-to-date system. We’ll guide you through the process of configuring Windows Update settings and ensuring that your system receives the latest updates and patches.
Chapter 6: Performance Optimization and Troubleshooting
To ensure optimal performance, Windows 7 provides tools and options for system optimization. We’ll discuss how to use the Performance Monitor, Resource Monitor, and the Windows Experience Index to assess and improve your system’s performance. Additionally, we’ll explore common troubleshooting techniques for resolving issues such as system crashes, application errors, and driver problems.
Chapter 7: Accessibility and Special Features
Windows 7 places a strong emphasis on accessibility, aiming to make computing accessible to users with various needs and preferences. We’ll explore the accessibility features built into the operating system, including the Ease of Access Center, Narrator, Magnifier, and speech recognition.
Special features like Windows Touch, designed for touch-enabled devices, and XP Mode, which enables compatibility with older applications, will also be covered in this chapter.
Conclusion:
Windows 7, with its intuitive interface, enhanced features, and robust security measures, remains a popular choice for many users even years after its initial release. This comprehensive guide has provided a thorough exploration of the essential aspects of getting started with Windows 7, from installation to customization, file management to security, networking to troubleshooting. Whether you’re a new user or someone looking to delve deeper into the capabilities of Windows 7, this guide serves as a valuable resource for making the most of this iconic operating system.