Mastering Digital Artistry: A Comprehensive Exploration of Vector Art vs. Raster Art in CorelDRAW with Tutorials

Introduction
In the realm of digital artistry, the choice between vector and raster art is a fundamental consideration that significantly impacts the creative process. CorelDRAW, a powerful vector graphics software, serves as a versatile platform for artists and designers, offering tools for both vector and raster-based creations. In this extensive article, we will embark on a comprehensive exploration of the distinctions between vector and raster art, and delve into CorelDRAW tutorials to master the techniques associated with each medium.
Understanding Vector Art
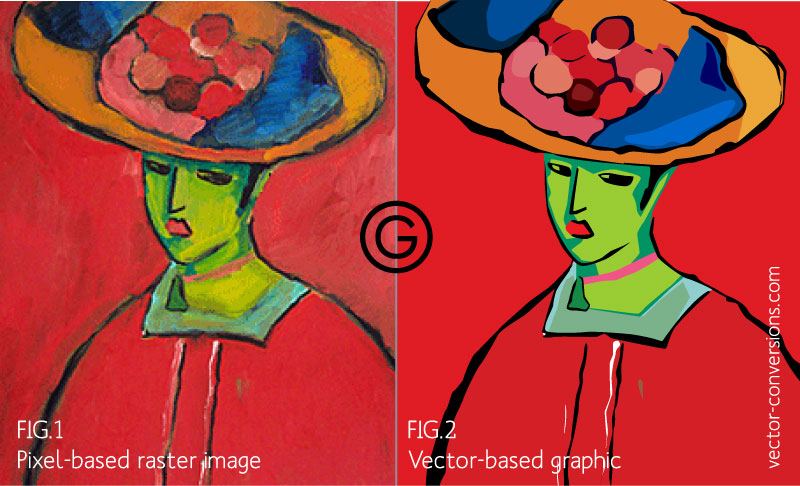
Vector art is a form of digital illustration that utilizes mathematical equations to define shapes and lines. These mathematical representations allow vector graphics to be infinitely scalable without losing quality. CorelDRAW excels in vector art creation, providing a suite of tools that cater to precision, scalability, and flexibility.
- Core Characteristics of Vector Art:
a. Scalability: Vector art can be resized without any loss of quality, making it ideal for projects that require scalability, such as logos, icons, and illustrations.
b. Editability: Vector objects in CorelDRAW are editable even after creation. This allows artists to modify shapes, colors, and other attributes seamlessly.
c. Clean Lines and Smooth Curves: Vector graphics are characterized by clean lines and smooth curves, providing a polished and professional appearance to the final artwork.
- CorelDRAW Vector Art Tutorial: Creating a Logo
To create a logo in CorelDRAW, follow these steps:
a. Sketching: Begin with a rough sketch of the logo design to plan the composition.
b. Vector Shapes: Use CorelDRAW’s shape tools to create the foundational elements of the logo.
c. Color and Styling: Apply colors, gradients, and styling to enhance the visual appeal.
d. Typography: Integrate text using vector-based fonts to complement the logo design.
e. Export: Save the logo in vector formats like SVG or AI for scalability.
Understanding Raster Art
Raster art, also known as bitmap or pixel-based art, is created using a grid of individual pixels. Each pixel contains specific color information, and when combined, they form detailed images. CorelDRAW’s robust suite extends its capabilities to raster art, offering features for photo editing, digital painting, and detailed illustrations.
- Core Characteristics of Raster Art:
a. Detail and Realism: Raster images excel in capturing intricate details and realism, making them suitable for digital paintings, photographs, and detailed illustrations.
b. Resolution Dependency: Unlike vectors, raster images are resolution-dependent. Enlarging them may result in a loss of quality.
c. Texturing and Shading: Raster art allows for intricate texturing, shading, and the application of various brush strokes, providing artists with a wide range of creative possibilities.
- CorelDRAW Raster Art Tutorial: Digital Painting
To create a digital painting in CorelDRAW, follow these steps:
a. Setting Up the Canvas: Create a new document and set the canvas size and resolution based on the intended use.
b. Brush Selection: Choose from CorelDRAW’s array of brushes, adjusting size, opacity, and hardness as needed.
c. Color Palette: Utilize the color picker and swatches to select a suitable color palette for the painting.
d. Layer Management: Organize your artwork by using layers for better control over elements.
e. Detailing and Shading: Add details, textures, and shading to enhance the depth and realism of the digital painting.
Comparing Vector and Raster Art in CorelDRAW
- Scalability:
- Vector Art: Infinitely scalable without loss of quality.
- Raster Art: Resolution-dependent, may lose quality when enlarged.
- Editability:
- Vector Art: Fully editable, allowing modifications to shapes and colors.
- Raster Art: Limited editability, especially with intricate details.
- Detail and Realism:
- Vector Art: Clean lines and shapes; ideal for logos and illustrations.
- Raster Art: Captures intricate details and realism; suitable for digital paintings and photographs.
- File Size:
- Vector Art: Generally smaller file sizes.
- Raster Art: Larger file sizes, especially for high-resolution images.
- Application:
- Vector Art: Logos, icons, illustrations, and designs requiring scalability.
- Raster Art: Digital paintings, photographs, and projects demanding detailed realism.
CorelDRAW Tutorials: Integrating Vector and Raster Art
- Creating a Composite Design:
- Combine vector and raster elements for a holistic design.
- Utilize vector shapes for logos and typography.
- Incorporate raster images for detailed backgrounds or textures.
- Exporting and Integrating:
- Export vector designs in scalable formats like SVG or AI.
- Export raster designs in common formats like JPEG or PNG.
- Integrate both formats seamlessly within a single project in CorelDRAW.
- Applying Effects and Filters:
- Experiment with CorelDRAW’s effects and filters for both vector and raster elements.
- Apply vector-based effects to enhance logos or illustrations.
- Utilize raster-based filters for creative enhancements in digital paintings.
- Advanced Techniques:
- Combine vector and raster elements using CorelDRAW’s layer management.
- Create a sense of depth by integrating detailed raster textures with vector shapes.
- Experiment with blending modes and transparencies to seamlessly merge both art forms.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the dynamic interplay between vector and raster art within CorelDRAW opens up a world of creative possibilities for artists and designers. By understanding the strengths and characteristics of each medium, artists can leverage CorelDRAW’s versatile tools to create captivating and well-balanced compositions. Whether crafting a scalable logo using vector precision or immersing in detailed digital paintings with raster intricacies, CorelDRAW stands as a powerhouse for both vector and raster artistry, providing a platform where imagination knows no bounds.